What is the Circuit breaker?
The circuit breaker is a crucial component in electrical systems that provides protection from overcurrent and short circuits.
It is a device that automatically interrupts electrical current flow when there is an excess of current or an unexpected surge in voltage.
It acts as a safety mechanism that prevents damage to electrical equipment and helps to minimize the risk of electrical fires.
Understanding its basics is essential for homeowners, electricians, and anyone who works with electrical systems.
In this blog post, we will explore the different types of circuit breakers, their functions, and how they are installed.
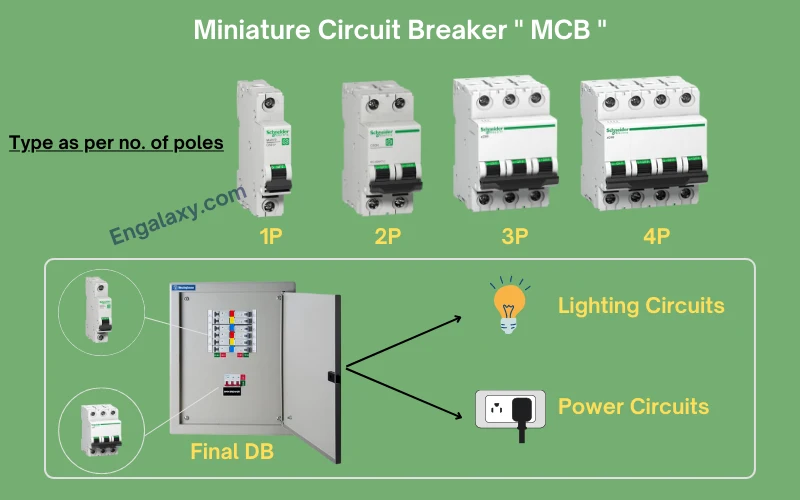
Miniature Circuit breaker
Miniature Circuit Breakers, or as abbreviated with MCBs, according to BS EN 60898, are suitable for operation by ordinary persons and have fixed protection settings, generally a two-position on/off the operating handle and a performance relative to the final circuits in an electrical installation.
They would normally be the final overcurrent protection measure in the electrical system, for example, before sockets or lighting circuits.
Typical current ratings are from 0.5 A to 125 A. Short-circuit ratings may be up to 25 kA.
Performance and testing are in accordance with BS EN 60898 for domestic and similar applications categorized by the trip characteristic types B, C & D.
MCBs may also be available with application-specific tripping characteristics.
MCBs may also be rated in accordance with BS EN 60947-2 for industrial or similar applications.
Summary of MCB:
- It has two positions only, ON or OFF.
- Its size is small.
- It can be single, double, triple, or Four poles.
- It has small values of short circuit capacities.
- It’s not adjustable, fixed only.
- Its trip unit type is thermomagnetic.
- Its cost is cheap.
- We use it in the final circuits, like lighting and power.
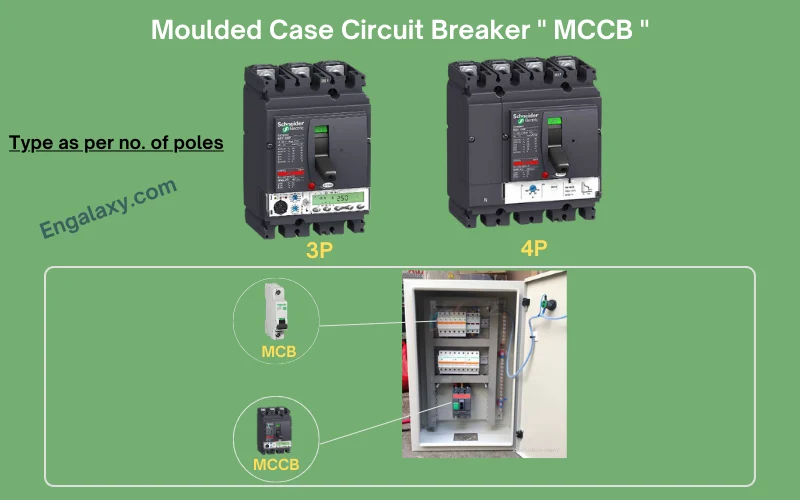
Moulded Case Circuit breaker
Moulded Case Circuit Breakers or as abbreviated with MCCBs, may have fixed or adjustable protection settings, normally a three-position toggle operating handle giving on-off-tripped indication plus reset function and a performance level relative to the incoming supply such that they can be installed at a point close to the supply transformer.
Typical current ratings are from 16 A to 1600 A though ratings up to 3,200 A are available, but it depends on the manufacturer’s standards.
Short-circuit ratings may be up to 100 kA. Performance and testing are in accordance with BS EN 60947-2.
Sometimes we use it as the main breaker, or it can be the breaker of branch circuits in other panels like SMDBs & MDBs.
Summary of MCCB:
- It has three positions, ON, OFF, or Trip.
- Its size is medium.
- It can be triple or Four poles.
- It has medium values of short circuit capacities.
- It can be fixed or adjustable.
- Its trip unit type can be thermomagnetic or Electronic.
- Its cost is not cheap.
- We use it sometimes in the branch circuits or as the main breaker in the panel.
- It can be motorized or not.
Air Circuit breaker
(ACBs) are normally used as the main incoming protection and have a spring-operated mechanism to open and close the device, often charged by an internal motor.
The protection settings will include time delays, and the devices will have a short-time withstand value to give full discrimination under fault conditions with downstream protection devices.
Typical current ratings are 630 to 6,300 A. Short-circuit ratings may be up to 150 kA.
Performance and testing are in accordance with BS EN 60947-2.
Summary of ACB:
- It has three positions, ON, OFF, or Trip.
- Its size is big.
- It can be triple or Four poles.
- It has high values of short circuit capacities.
- Its type is adjustable.
- Its trip unit type can be thermomagnetic or Electronic.
- Its cost is expensive.
- it can be a withdrawable type.
- We use it sometimes in the branch circuits or as the main breaker in the panel.
- It can be motorized or not.
Expert Advice:
Whenever you’re ready to learn about Electrical systems, this includes cables, equipment, 1st fix, 2nd fix, and 3rd fix. There are 2 ways we can help you:
1- Enroll now in this Electrical Online course and watch more than 50 lectures; more new lectures will be added.
Or
2- Enroll now in this and get immediate access to more than 170 lectures in our different online courses. Plus, during your subscription, you will get access to all the new future courses & lectures added to the package.
You can get your 24 Hours trial today for just $3 and get access to all courses. You can cancel your subscription at any time.
Note: We offer you 14-Day Money Back Guarantee if you don’t like the course
Also, if you would like to read more about our blog posts, you can find all of them on this link:
You can have a look at our Free MEP Course from the below link:
https://link.urcoursez.com/freemep